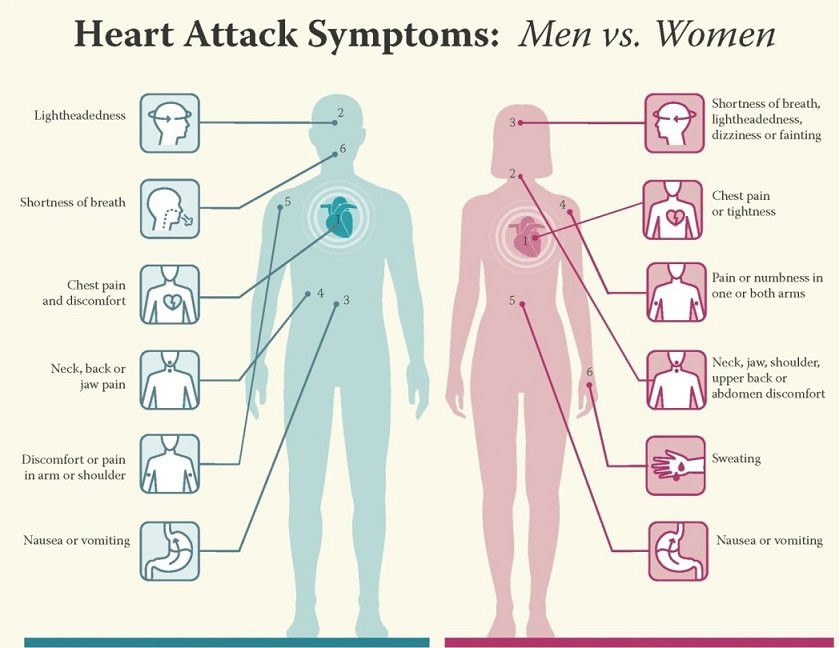
What are the signs of a heart attack?
Heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, are a prevalent and life-threatening cardiac condition. Various factors, including hypertension, obesity, and diabetes, can trigger them. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate actions is essential for timely treatment and increasing the chances of survival.
Many people often mistake the symptoms of a heart attack for those of digestive disorders or costochondritis. Therefore, knowing the key indicators and causes of heart attacks is crucial.
Causes of Heart Attacks:
Type I Heart Attack occurs when plaque accumulates on the inner walls of the heart and blood vessels, restricting blood flow & increasing the heart's ability to pump blood.
Type II Heart Attack: This happens when the coronary artery doesn't receive sufficient oxygen, causing temporary death of cardiac muscle tissues and resulting in myocardial infarction.
Drug Misuse: Certain drugs containing components like alprazolam or clonazepam can also trigger heart attacks.
Identifying a Heart Attack:
Chest Pain: Pain in the left or central part of the chest, near the sternum, can be a sign of a heart attack, although other conditions can also cause it.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing due to the heart's inability to pump blood efficiently into the lungs.
Pain Radiating in the Left Arm: Severe pain radiating along the left arm can indicate a heart attack.
Excessive Sweating: Increased body temperature due to inadequate heat distribution can cause profuse sweating.
Dizziness and Blurred Vision: Reduced oxygen supply to the brain can lead to dizziness and blurred vision.
Actions to Take:
If you suspect someone is having a heart attack, immediately take them to the hospital. Use an oximeter to check their oxygen levels; if it's below 80, they require urgent oxygen support, as this could lead to heart failure.
Conclusion:
It's essential to differentiate the symptoms of a heart attack from those of indigestion or angina. Factors like depression, stress, obesity, and high blood pressure increase the risk of a heart attack. For more information, consult a healthcare professional or visit a hospital's website.